Expressvpn Glossary
Biometric authentication

What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is a security process involving the use of biological or behavioral data to verify a person’s identity. Common examples include fingerprint scans and facial recognition technology. Biometric authentication offers a secure and convenient alternative to conventional authentication methods, like passwords.
How does biometric authentication work?
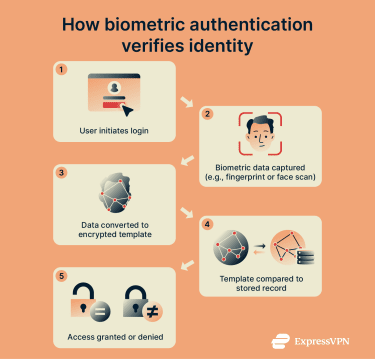
First, biometric data is collected from the user and converted into an encrypted mathematical template for future reference. Then, when the user attempts to log in using biometrics, a four-step process begins:
- Data capture: The user’s biometric data is collected, like their fingerprint data via a fingerprint scanner.
- Data conversion: The data is converted into an encrypted template, as it was during the initial set-up phase.
- Matching process: The new template is compared to the old one to see if the two match.
- Decision: If the two templates match, access is granted. If not, access is denied.
Common types of biometric authentication
Biometric authentication comes in several forms, each using unique physical or behavioral traits to verify identity. Fingerprint recognition, for example, scans the distinctive patterns on a person’s fingertip, while facial recognition analyzes the size and shape of facial features.
Iris and retina scans focus on the intricate patterns in specific parts of the eye, providing another highly secure method of identification. Voice recognition, on the other hand, examines the pitch and tone of a person’s voice.
Beyond physical traits, behavioral biometrics looks at patterns in how people move or interact with objects, such as their gait, handwriting, or typing style.
Why is biometric authentication important?
Biometric authentication can reduce or even eliminate the need for passwords to protect accounts and data, improving account security with the use of unique identifiers that are very difficult to forge, steal, or imitate.
This mode of authentication is also more convenient for users; rather than having to create multiple complex and unique passwords, they can simply use their fingerprint or face to access their accounts or unlock devices.
Biometric authentication is a key component of multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems, and it provides more secure access to everything from mobile devices to online bank accounts and social media profiles.
Security and privacy considerations
Biometric authentication requires the collection of biometric data. While legitimate companies use measures like encryption and secure servers to keep biometric data safe and adhere to relevant data regulations, users should be aware of the risks of data leaks, breaches, and losses.
Users should also understand that despite its security benefits, biometric authentication is not a perfect security method. Additional steps should be taken to secure data and connections, like using additional factors to authenticate.
Common use cases
Biometric authentication is applied across many industries and everyday applications to enhance security and streamline access. It’s commonly used for:
- Device authentication: Access to smartphones and laptops.
- Online banking and payments: Secure payments and account access.
- Border controls: Verifying traveler identities at airports and border crossings.
- Workplace security: Secure access to systems and facilities.
Further reading
- What is biometrics? A complete guide to modern identity technology
- What is two-factor authentication (2FA), and how to set it up securely
- Biometric data collection around the world
- Biometrics security in ExpressKeys for iOS
FAQ
What makes biometric authentication secure?
Biometric authentication uses unique physical or behavioral traits that are very difficult to either steal or imitate, making it much harder for attackers to gain access to data or accounts protected in this way.
Can biometric data be stolen?
Yes, it’s possible for biometric data to be stolen through cyberattacks targeting the databases where it’s stored.
Can biometrics work offline?
Yes, it’s possible for biometric data to be stored locally on a device, allowing for authentication even if the device is offline.
