Expressvpn Glossary
Data validation

What is data validation?
Data validation is the process of ensuring that data is accurate, consistent, and meets defined quality standards before being used or stored. It verifies that data falls within allowed ranges, follows required formats, and complies with organizational validation rules.
This step helps maintain data integrity and reliability across systems, especially in large-scale data management and AI applications.
How does data validation work?
Data validation works by applying predefined rules and checks to ensure data is logical, consistent, and correctly formatted before being stored or used. These rules may verify data type, range, format, uniqueness, or the presence of required fields.
Validation can occur at multiple stages (such as during data entry, system integration, or database storage) to confirm that all data remains accurate and compatible across systems. Modern platforms often automate these checks, reducing human error and improving workflow efficiency.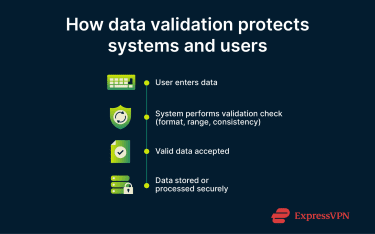
Why is data validation important?
Data validation is important for several reasons:
- Ensures data accuracy and reliability: Confirms that data follows the correct structure, range, and format before use.
- Prevents security vulnerabilities: Blocks unsafe inputs that could trigger attacks like Structured Query Language (SQL) injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Supports compliance: Enforces data protection and privacy requirements through proper validation controls.
- Builds operational trust: Reduces data-related errors and keeps systems stable and efficient.
- Improves AI and analytics performance: Provides clean, consistent data for effective model training and analysis.
Types of data validation
Data validation can take several forms, depending on the type of information being checked and the rules applied.
- Format validation: Ensures data follows the required pattern, such as a date in mm/dd/yyyy format or the presence of an “@” symbol in an email address.
- Range validation: Confirms that numerical values or dates fall within defined limits to prevent impossible or invalid entries.
- Consistency validation: Verifies that related fields align logically, such as ensuring a start date precedes an end date.
- Cross-field validation: Checks that entries in multiple fields don’t conflict, such as matching passwords or verifying that a billing address matches the selected country.
- Code-based validation: Uses custom scripts or functions to enforce complex rules beyond standard validation checks.
Data validation in cybersecurity
Data validation is a critical aspect of a strong cybersecurity posture, serving as a first line of defense against injection attacks and malicious payloads. By ensuring input data adheres to defined rules, it helps prevent unauthorized data manipulation and system exploitation.
The practice often works alongside encryption and authentication mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information transmitted or stored via web applications, APIs, and database management systems. Because such systems frequently accept user-entered or machine-generated data, embedding validation checks helps ensure malicious or malformed data can’t penetrate deeper layers of the infrastructure
Further reading
- Data scraping: What it is and how it works
- What is a bot? Are bots dangerous? Everything you need to know
- What is data encryption?
FAQ
What is data validation used for?
Data validation is used to ensure that inputted data is complete and formatted accurately. The rules are set up to prevent mistakes, incomplete information, or malicious inputs.
How does data validation help with cybersecurity?
Data validation rejects harmful or unexpected data before it reaches the database or backend. This prevents cyberattacks like Structured Query Language (SQL) injection and cross-site scripting (XSS) that exploit poorly filtered data. It can also prevent malicious file uploads by limiting attachments to specific file types or sizes.
What’s the difference between data validation and data verification?
Data validation confirms that data meets the required rules and format for its intended use. It ensures that information is structured, accurate, and complete before being stored or processed.
Data verification confirms that data remains accurate and consistent after transfer or processing. It checks that the information in one system matches the original source or reference data.
