Expressvpn Glossary
ipconfig

What is ipconfig?
ipconfig is a command-line utility tool used in Windows operating systems to display network configuration information, including IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6), Domain Name System (DNS) settings, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocols (DHCP), and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (IP) values.
What does ipconfig do?
ipconfig commands can be used for the following reasons:
- View IP address: ipconfig parameters can reveal the IPv4 and IPv6 addresses of network devices and adapters.
- Release and renew DHCP IP: ipconfig parameters can be used to change connected devices’ public IP addresses, often automatically assigned by an internet service provider (ISP).
- Flush DNS: ipconfig commands can be used to purge and flush DNS cache on network devices and adapters.
- View other network configuration data: ipconfig parameters allow network admins and users access to configuration data such as subnet mask and default gateway.
The table below shows some crucial ipconfig parameters and what they do:
| ipconfig parameter | Functionality |
| /all | Outputs complete TCP/IP configuration on all network adapters |
| /displaydns | Displays DNS client resolver cache contents |
| /release | Releases the current DHCP-assigned IP address for all adapters (or a specified adapter) |
| /renew | Renews the DHCP lease, obtaining a new IP address from the DHCP server |
| /? | Outputs help (including all other available commands) |
When should you use ipconfig?
Some of the most common use cases for ipconfig include:
- Troubleshooting network issues: ipconfig may help identify the cause of network connectivity issues.
- Diagnosing DNS or IP problems: ipconfig can show certain IP or DNS issues, such as two network devices using the same IP address or outdated DNS settings.
- Refreshing IP: Old IP addresses can be released so another one is assigned automatically by the DHCP using ipconfig.
- Resolving slow connection issues: ipconfig can be used to check which DNS servers a device is using. Then the ping command can test those servers to see if they’re responding slowly. If needed, switching to a faster DNS server can improve connection speed.
ipconfig vs. ifconfig
ipconfig and ifconfig are similar command lines that display network configuration parameters, but they work differently. ipconfig is mainly used in Windows operating systems, while ifconfig finds application in Unix-based systems, such as macOS and Linux, even though it has been officially deprecated for the ip suite.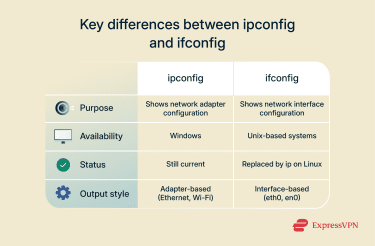
Further reading
- How to change IP address on Android
- How to change IP address on iPhone
- How to configure a static IP address
FAQ
What is ipconfig used for?
ipconfig is used to retrieve network configuration information, which can help troubleshoot or optimize network setups or provide greater visibility into a network.
How do I run ipconfig on Windows?
ipconfig can be run on Windows by entering the command line into the cmd.exe terminal. The basic command, without using any parameters, displays the IP address, default gateway, and subnet mask for all network adapters found on the network.
What does ipconfig /all show?
The ipconfig /all command shows the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) / Internet Protocol (IP) configuration settings for adapters connected to a network, whether or not the adapters are enabled.
What’s the difference between ipconfig and ifconfig?
ipconfig is a Windows-based command line used to display network configuration settings, while ifconfig does the same for Unix-based operating systems like macOS and Linux.
Does ipconfig work on Mac?
ipconfig works on Mac, but the base command alone won’t return results like on Windows devices. Instead, the [man ipconfig] command can be run in the macOS terminal to return appropriate ipconfig commands for various network troubleshooting, diagnostics, configuration, and visibility operations.
