Expressvpn Glossary
Webpage
What is a webpage?
A webpage is a single document on the internet that displays content through a web browser. It can contain text, images, videos, links, and interactive elements. Each webpage exists at a specific web address (URL) and serves a particular purpose, such as providing information or facilitating transactions. Webpages are the basic building blocks of every website.
How does a webpage work?
When a user enters a URL or clicks a link, the browser sends a request to a web server. The server responds by delivering the webpage’s files to the device. The browser interprets these files and renders them on screen. HTML defines the structure, CSS controls the design, and JavaScript traditionally handles the logic that makes webpages interactive and responsive.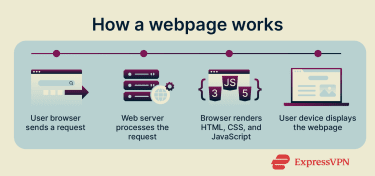
In modern websites, JavaScript does much more than enable interactivity. Frameworks like React or Angular use it to build and update entire page layouts, load data dynamically, and connect to complex web applications. As a result, many webpages won’t display or function properly if JavaScript is disabled.
This exchange of data between the browser and the server happens over the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) or Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) protocol. HTTPS adds encryption so that information transmitted between the browser and the server remains secure, which is essential for webpages that handle passwords, payments, or any other sensitive data.
Types of webpages
Different webpages serve different functions:
- Static webpages: Display fixed content that remains the same for all visitors. They are simple to create and quick to load.
- Dynamic webpages: Change content in real time based on database queries or user interactions. Examples include social media feeds and product listings.
- Landing pages: Focus on a single topic or goal, such as account registration or downloading a resource.
Parts of a webpage
Most webpages share common structural components that help organize content and improve usability:
- Header: Contains the site title, logo, and navigation menu.
- Main content area: Displays the primary information, including text, media, and interactive elements.
- Sidebar: Often appears beside the main content area, providing supplementary links, widgets, or advertisements.
- Footer: Located at the bottom of the page, usually within the main content area, and includes contact information, navigation links, and legal notices.
Why are webpages important?
Webpages are the foundation of online communication and information exchange. They connect people to services, businesses, and digital resources. Companies use webpages to sell products, deliver customer support, and establish an online presence. Educational institutions use them to share materials and announcements.
Webpages also enable access to essential services such as news, banking, and healthcare. Their structure and security determine how safely and efficiently users interact with online content. For example, using HTTPS prevents data interception, while unsecured links may expose sensitive information.
Further reading
- What is cybersecurity? A simple guide for beginners
- What is a firewall and how does it work
- How does the internet work?
FAQ
What is the difference between a webpage and a website?
A webpage and a website are related but distinct. A webpage is a single document, while a website is a collection of interconnected webpages that share one domain name.
For instance, expressvpn.com is a website consisting of multiple webpages, such as the homepage, features pages, and blog posts. Each webpage has its own URL but belongs to the same website.
How are webpages created?
Webpages are created using HTML code to define structure and content. Developers add CSS to control appearance and JavaScript to add interactive features. Many people now use content management systems or website builders that generate this code automatically, making webpage creation accessible without extensive coding knowledge.
What makes a webpage secure?
A secure webpage uses HTTPS instead of HTTP. HTTPS encrypts data transmitted between browsers and the web server. Secure pages can be identified by the padlock icon in the browser's address bar.
