Comprehensive guide to network security standards and compliance

In today’s hyper-connected world, networks form the foundation of how organizations operate and share information. As connectivity expands, so does the need for consistent, reliable security practices that protect data and maintain trust.
Network security standards make this possible, providing the frameworks, protocols, and guidelines needed to protect networks from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats.
This guide explores what network security standards are and why they matter, highlighting some of the most important standards and frameworks of today.
Understanding network security standards
Before diving into specific network security standards like the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework (NIST CSF) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) / International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 27001 standard, it’s helpful to understand what these standards are and why they exist.
In simple terms, network security standards are sets of rules, best practices, and recommended steps that organizations follow to protect their networks, devices, and data.
Network security standards give organizations clear, structured frameworks to guide their cybersecurity practices. Without them, approaches to network security could vary widely, creating inconsistencies and potential vulnerabilities for cybercriminals to exploit.
Standards provide the vital frameworks organizations around the world need to figure out how to keep their sensitive data safe and private. They cover everything from which encryption protocols to use for specific types of networks to firewall configuration standards so that even non-technical teams know what they need to do regarding cybersecurity.
Network security standards are also vital for organizations to comply with any relevant rules or regulations they might be subject to, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Following these standards helps organizations protect sensitive data responsibly while staying compliant with industry and legal expectations.
Key benefits of implementing standards
Implementing network security standards is imperative for organizations today when it comes to strengthening network defenses, mitigating the risk of cyberattacks, and complying with regulations. Here’s a closer look at some of the most significant benefits.
Strengthening overall security posture
A primary goal of network security standards is to improve defenses against digital threats. They guide organizations in putting the right tools, controls, and protocols in place to reduce vulnerabilities and enhance overall security.
Many standards instruct organizations on ways to safeguard sensitive data, for example, through the use of encryption protocols and other tools, like Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC). Organizations that follow these standards can better prevent data loss, breaches, malware infections, and other security incidents.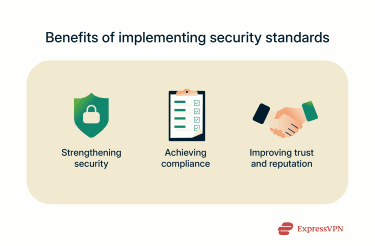
Achieving regulatory and legal compliance
Many industries face strict regulations governing the collection, storage, and management of data. In healthcare, for example, organizations must handle patient data and medical records with particular care.
Standards are often designed with these compliance frameworks in mind. They help organizations, particularly those in high-risk industries that deal with a lot of sensitive data, like finance, healthcare, and law, to comply with relevant rules and avoid penalties or other legal consequences.
Building trust with customers and stakeholders
Organizations that adhere to network security standards demonstrate a commitment to cybersecurity, which can strengthen trust with customers and stakeholders. Clear standards signal that a company is proactively managing risks and protecting sensitive information.
By contrast, organizations that don’t follow recognized standards may leave themselves more exposed to security incidents, which can erode trust and make customers or partners hesitant to engage.
Major types of network security standards
There are two main types of network security standards: compliance-focused standards, which outline specific rules and regulations organizations need to abide by, and technical standards, which lay out the best practices, security controls, and protocols to use to meet those compliance goals.
In simpler terms, compliance standards define what organizations need to do, and technical standards tell them how to go about it.
Compliance frameworks
Many industries must comply with strict national or international regulations regarding how they collect, store, and use data. Compliance-focused standards essentially instruct organizations on how they should keep their data, and that of their customers or users, safe.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS)
As online payments become more common, businesses that handle sensitive payment information (such as credit card numbers) must do so securely. PCI-DSS is a global standard, developed by leading credit card companies, to keep cardholder data safe during online transactions.
The standard outlines core security requirements, including encryption, access controls, and network monitoring. PCI-DSS is critical for reducing fraud and preventing unauthorized access to payment information. Any organization that processes, stores, or transmits cardholder data should follow this standard.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a U.S. federal law and regulatory framework, focused exclusively on the healthcare industry. It applies to covered entities (such as hospitals, clinics, and health insurers) and their business associates, and governs how they handle sensitive patient information, including medical records and laboratory results.
HIPAA requires organizations to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI), helping prevent identity theft, fraud, and data breaches.
While HIPAA directly applies to U.S. covered entities, non-U.S. organizations can become subject to HIPAA requirements, too, if they act as business associates through contracts with U.S. covered entities.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is an EU data privacy regulation that applies to any organization (inside or outside the EU) that processes personal data of EU and European Economic Area (EEA) residents.
GDPR focuses largely on transparency when it comes to how companies collect, store, and use people’s data. Organizations must clearly inform individuals about what data is being collected and why, and must process that data on the basis of a valid lawful basis (such as consent, performance of a contract, legal obligation, vital interests, public task, or legitimate interests). It also grants individuals rights over their personal data, including the ability to request its deletion. Noncompliance can result in substantial fines and penalties.
Industry and technical standards
The industrial and technical standards listed below typically go into greater detail about which specific tools, protocols, and practices organizations should employ to strengthen their security and comply with the regulations seen above.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The NIST CSF contains a flexible set of guidelines that organizations can follow to minimize their cybersecurity risks. The framework is oriented around six core pillars: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover, and Govern.
Many U.S. government agencies, large enterprises, and critical infrastructure providers follow this framework, in conjunction with other security standards, to guide risk assessment, threat management, and incident response planning.
ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27033
ISO/IEC 27001 focuses on information security management systems (ISMS). It outlines how organizations can manage data securely, ensuring confidentiality and integrity without compromising accessibility. It covers areas such as risk assessment, asset management, and incident response.
ISO/IEC 27033 specifically addresses network security, offering detailed guidance for designing and implementing secure network architectures. It covers topics like risk assessment, which network security controls to use, and how to work with important network security tools like the Internet Protocol Security (IPsec).
IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi security standards)
Developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, IEEE 802.11 defines standards for wireless local area networking (Wi-Fi), including security protocols like Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3). IEEE 802.11 is a fundamental standard for enabling secure connectivity between devices.
CIS controls
The Center for Internet Security (CIS) Critical Security Controls provide a prioritized set of best practices that organizations can follow to defend against cyberattacks. Unlike frameworks focused on risk assessment and management, CIS Critical Security Controls emphasize specific actionable steps, such as implementing anti-malware defenses, secure configuration practices, and access control measures, to reduce exposure to threats.
Best practices for implementing network security standards
Network security standards provide the frameworks organizations need to establish strong network security. Think of them as instruction manuals that guide organizations on how to protect their networks. But even the best instructions only work if you follow them carefully, using proven techniques and best practices.
Building security policies and dedicated teams
To enjoy consistently strong network security, organizations need to establish two crucial, fundamental pillars: strong security policies and dedicated teams to enforce them.
Starting with policies, take the time to set out, in detail, how you intend to operate and administrate your networks. Think about data handling, access management, and incident responses, giving your organization and your teams the clear and concise rules they need to follow to maintain network security and respond to new threats as they emerge.
Next, build teams (or outsource them, depending on your business’s needs and budget) to enforce policies consistently. Teams should have the necessary expertise and clearly defined roles, from monitoring compliance to responding to incidents.
Risk assessment and ongoing monitoring
Cybersecurity is an ever-changing landscape, with new threats constantly emerging. Regular risk assessments are essential to stay ahead. Never assume your network security has reached a “perfect” state, as there are almost always improvements to be made.
Use international frameworks of risk assessment and management to analyze emerging threats and improve your digital defenses. Examples include the NIST SP 800-30, ISO 27005, and Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR) methodology.
Also get into the habit of monitoring your networks in real-time with the use of security tools. Helpful options include intrusion detection systems (IDS), intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions.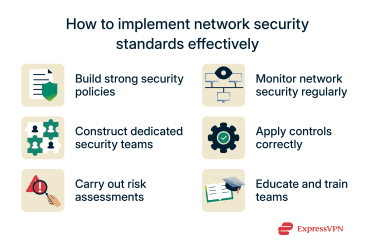
Applying security controls effectively
Security controls form the technological backbone of network security. These include firewalls, encryption keys, virtual private networks (VPNs), and IPSs. They enforce security policies, protect data, and assist with compliance.
But these tools and controls can vary in their performance, depending on how well you deploy and configure them. Ensure that every security control you utilize is implemented effectively, starting with correct configuration and testing, followed by strict monitoring and iteration to optimize performance.
Employee training and awareness
Even the strongest technological defenses can be compromised by human error. Network security relies not only on tools like Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) / Transport Layer Security (TLS) encryption and the IPsec protocol but also on people.
Employees need to have the necessary knowledge to enforce network security standards. They may require training and access to helpful resources to ensure they’re ready to react if and when incidents occur and to restrict their own chances of causing network problems. Making them aware of phishing attacks and safe data handling, for example, is key.
Emerging trends in network security standards
The cybersecurity world is always evolving, with network security standards and frameworks regularly updated to embrace new technologies and counteract emerging threats. This section explores some of the most significant trends to keep an eye on
Zero-trust network access (ZTNA)
Zero trust is a security strategy that essentially revolves around one simple rule: never trust, always verify. In other words, it assumes that no user or device should be trusted by default and that every access request must be authenticated.
Applied to networks, zero-trust network access (ZTNA) enforces this principle, requiring verification for every user and device on the network. Some universal ZTNA systems extend zero trust to all access points, controlling access strictly and minimizing the network’s attack surface, thereby reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data loss.
AI and machine learning for compliance
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (ML) technologies are playing an increasingly important role in cybersecurity on the whole and may be used to improve network security and compliance with strict data regulations, like GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST.
AI models can monitor network logs, configurations, and key metrics in real time, identifying policy violations or suspicious activity. Some systems can even take automated corrective actions, perform risk assessments, generate reports, and predict potential future compliance gaps, helping organizations stay proactive rather than reactive.
Secure access service edge (SASE)
Secure access service edge (SASE) is a cloud-based architectural model that integrates network connectivity and security. It enables secure, low-latency access from any location without routing all traffic through centralized data centers.
It provides a scalable and speedy option for companies that are heavily invested in cloud infrastructure, along with those that have many hybrid or remote workers.
WPA3 and next-generation wireless security
WPA3 is the latest Wi-Fi security protocol, following on from WPA2. It improves security in both password-protected and open wireless networks.
On password-protected networks, WPA3 strengthens authentication by making password-guessing and offline attacks more difficult. On open networks, it introduces opportunistic wireless encryption (OWE), which encrypts traffic even when no password is required.
As legacy WPA2 devices become less prominent, WPA3 should become the minimum security standard for wireless networking, ushering in an age of stronger network security for countless devices and their users around the world.
FAQ: Common questions about network security standards
What are network security standards in simple terms?
Put simply, network security standards are like rulebooks or instruction manuals that outline how networks should function in a secure and reliable way. They provide clear frameworks that organizations use to keep their digital data safe and prevent unauthorized access to their networks and devices. Well-known examples come from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Center for Internet Security (CIS).
What happens if organizations fail to follow security standards?
Organizations that fail to follow security standards are at risk of numerous problems and penalties. They are more prone to cyberattacks that could cause sensitive data, such as customer names, addresses, and payment details, to leak or end up on the dark web. This, in turn, can erode trust in the company and damage its reputation.
Organizations may also face fines and even legal repercussions if they fail to comply with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
How can companies ensure compliance with network security standards?
There are many ways companies can ensure compliance with network security standards. Recommended best practices include establishing a strong foundation of security policies that all employees must abide by, as well as conducting regular risk assessments and audits to assess how well the company is meeting its security goals. It’s also wise to continuously seek to improve and update your security policies and workflows to build a security-conscious culture.
What ISO standards are relevant for network security?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) / International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 27001 and ISO/IEC 27033 standards are both relevant when it comes to network security. 27001 is the world’s leading security standard for information security management systems, while the latter outlines best practices for designing secure internal and external network architectures.
What is the NIST standard for network security?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standard for network security is the Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). Designed to protect critical infrastructure in the U.S., like energy, water, and communications, it focuses on threat assessment and risk management, guiding both public and private organizations on how to both identify cybersecurity risks and respond to them.
What is the difference between compliance frameworks and security standards?
While there is some overlap between security standards and compliance frameworks, they are two distinct, separate concepts. Compliance frameworks outline the rules and processes organizations should follow to abide by legal or industrial regulations, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Security standards, meanwhile, provide information about specific controls and best practices for organizations to strengthen their security and protect data from leaks and breaches.
How often should network security standards be updated or reviewed?
It varies, depending on the nature of the organization’s work and other factors, but it’s generally recommended to review data privacy policies and network security standards on an annual basis. Organizations should also consider updating their standards if they undergo significant changes, like expansions, mergers, or investments in new technological infrastructure, or if regulatory requirements of their industry are updated.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN